Multimodal Analysis of Neurodegenerative Diseases
Utilization of Machine Learning Algorithms and Modeling on Genetic and Medical Cohort Data for Neurodegenerative Diseases
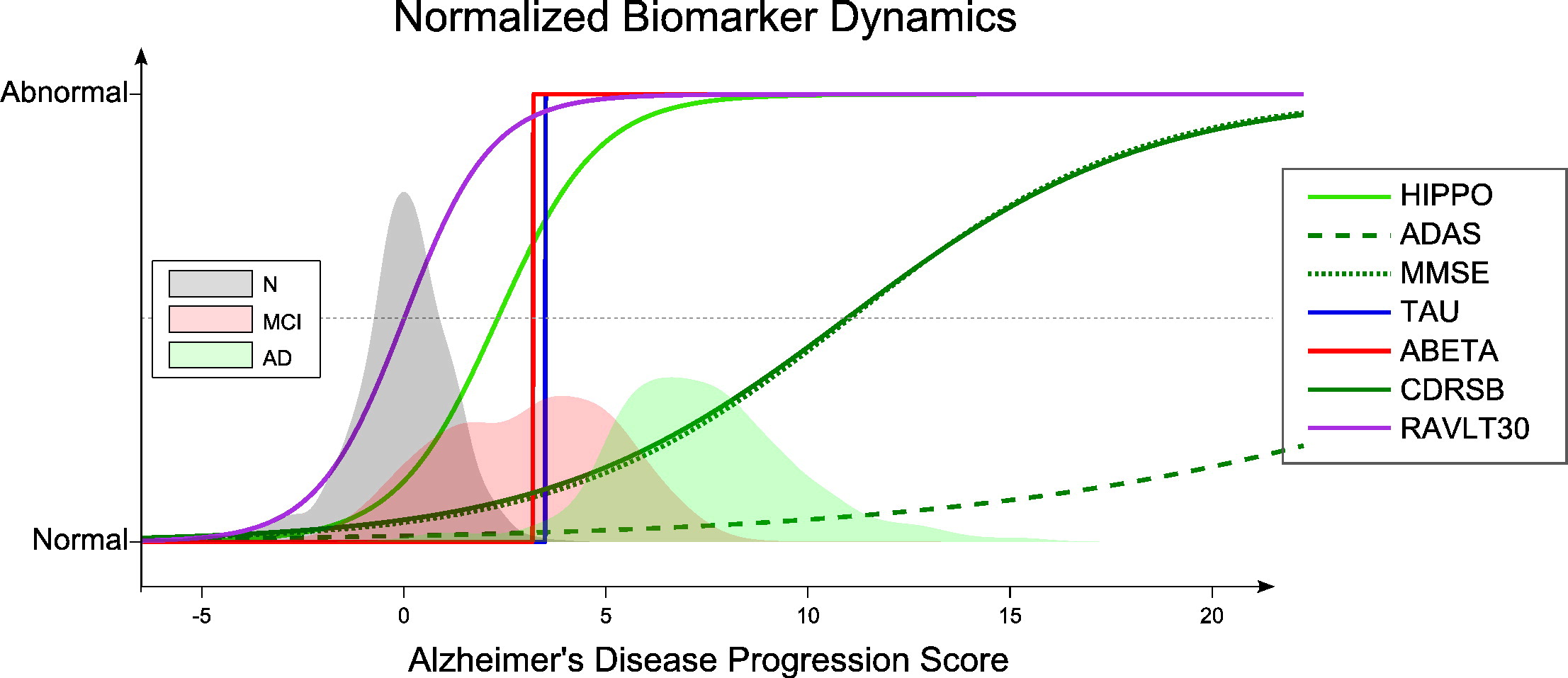
Utilization of Machine Learning Algorithms and Modeling on Genetic and Medical Cohort Data for Neurodegenerative Diseases
The Importance of Machine Learning Algorithms
-
Early Prediction and Diagnosis: Machine learning algorithms can analyze complex and voluminous genetic and brain imaging data, facilitating the early diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases. Early diagnosis allows clinicians to implement more effective interventions during the initial stages of the disease, potentially slowing its progression. Early diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s is crucial because these conditions typically progress slowly and might not show significant symptoms until considerable brain damage has occurred. Machine learning algorithms, by processing and analyzing massive datasets, can detect subtle patterns and anomalies in genetic and imaging data that might not be apparent through traditional analysis methods. This can lead to the identification of disease markers and early signs long before clinical symptoms appear, enabling earlier and potentially more effective therapeutic interventions.
-
Identification of Biomarkers: Advanced machine learning models can identify new biomarkers for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. These biomarkers can serve as critical indicators in predicting disease progression and evaluating the efficacy of treatments. Biomarkers are measurable indicators of a biological condition or disease. In the context of neurodegenerative diseases, biomarkers can include genetic markers, proteins, or changes in brain structure observed through imaging. Machine learning algorithms can sift through vast amounts of data from studies like ADNI and PPMI to find correlations and patterns that might indicate the presence or progression of a disease. Identifying reliable biomarkers is essential for developing diagnostic tools, monitoring disease progression, and tailoring individualized treatment plans.
-
Analysis of Multi-Modal Data: Cohort data from ADNI and PPMI include genetic information, brain imaging, clinical data, and other biological metrics. Machine learning algorithms can integrate and analyze these multi-modal datasets to uncover complex disease patterns. Multi-modal data refers to data collected from multiple sources or modalities, providing a comprehensive view of the subject. In the case of neurodegenerative diseases, this might include genetic data, MRI scans, PET scans, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers, and clinical assessments. Machine learning algorithms can merge these diverse data types to create a holistic model of the disease, identifying intricate relationships between genetic markers, brain changes, and clinical symptoms. This integrative approach can yield insights that are not possible from analyzing each data type in isolation.
-
Personalized Treatment: Machine learning facilitates the creation of personalized predictive models that can help determine individualized treatment plans. This approach can improve treatment outcomes and reduce side effects. Personalized medicine aims to tailor medical treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient. By using machine learning to analyze genetic, clinical, and other relevant data, it’s possible to predict how different patients might respond to various treatments. This can lead to more effective and less invasive treatment plans. For example, a machine learning model might predict that a particular drug is likely to be effective for a patient based on their genetic profile and disease stage, while another patient might benefit more from a different treatment strategy. Personalized treatment plans can optimize therapeutic efficacy and minimize adverse reactions.
Advantages of Using Cohort Data
-
Comprehensive and Standardized Data: Cohorts like ADNI and PPMI collect comprehensive and precise data from various patients, including genetic, brain imaging, clinical evaluations, and other biological metrics. These data are standardized and ready for advanced analysis. Cohorts like ADNI and PPMI are large-scale, multicenter studies designed to collect and standardize data across numerous subjects. The data collection protocols are rigorously defined to ensure consistency and reliability across different sites and time points. This standardization facilitates high-quality, reproducible research and allows for meaningful comparisons across studies. Comprehensive datasets enable researchers to perform in-depth analyses and develop robust machine learning models.
-
Large Sample Sizes: These cohorts include substantial numbers of patients and control samples, enhancing the statistical power of studies and enabling more complex and precise analyses. Large sample sizes increase the statistical power of research studies, allowing for the detection of smaller effects and more reliable findings. In the context of machine learning, larger datasets enable the development of more accurate and generalizable models. ADNI and PPMI provide access to thousands of patient records, including those from individuals at various stages of disease progression and from healthy controls. This diversity in the dataset helps in training machine learning models that can accurately predict disease outcomes and identify relevant biomarkers.
-
Access to Longitudinal Data: One of the significant advantages of these cohorts is the availability of longitudinal data, which allows researchers to examine changes in biological and clinical parameters over time. This information is invaluable for modeling disease progression and assessing the efficacy of treatments. Longitudinal data tracks the same subjects over extended periods, providing insights into the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. Such data can reveal how biomarkers and clinical symptoms change as the disease advances. Machine learning models can leverage longitudinal data to predict future disease states and evaluate the long-term effects of therapeutic interventions. This dynamic perspective is critical for understanding the natural history of neurodegenerative diseases and developing effective treatment strategies.
-
Facilitation of International Collaborations: Data from ADNI and PPMI are publicly accessible to researchers worldwide, facilitating international collaborations in neurodegenerative disease research. Open access to high-quality datasets like ADNI and PPMI promotes transparency and collaboration among researchers globally. By sharing data, scientists can validate findings, combine datasets for meta-analyses, and develop more powerful machine learning models. International collaborations enhance the robustness and applicability of research findings, accelerate scientific discovery, and foster innovation in the field of neurodegenerative disease research.
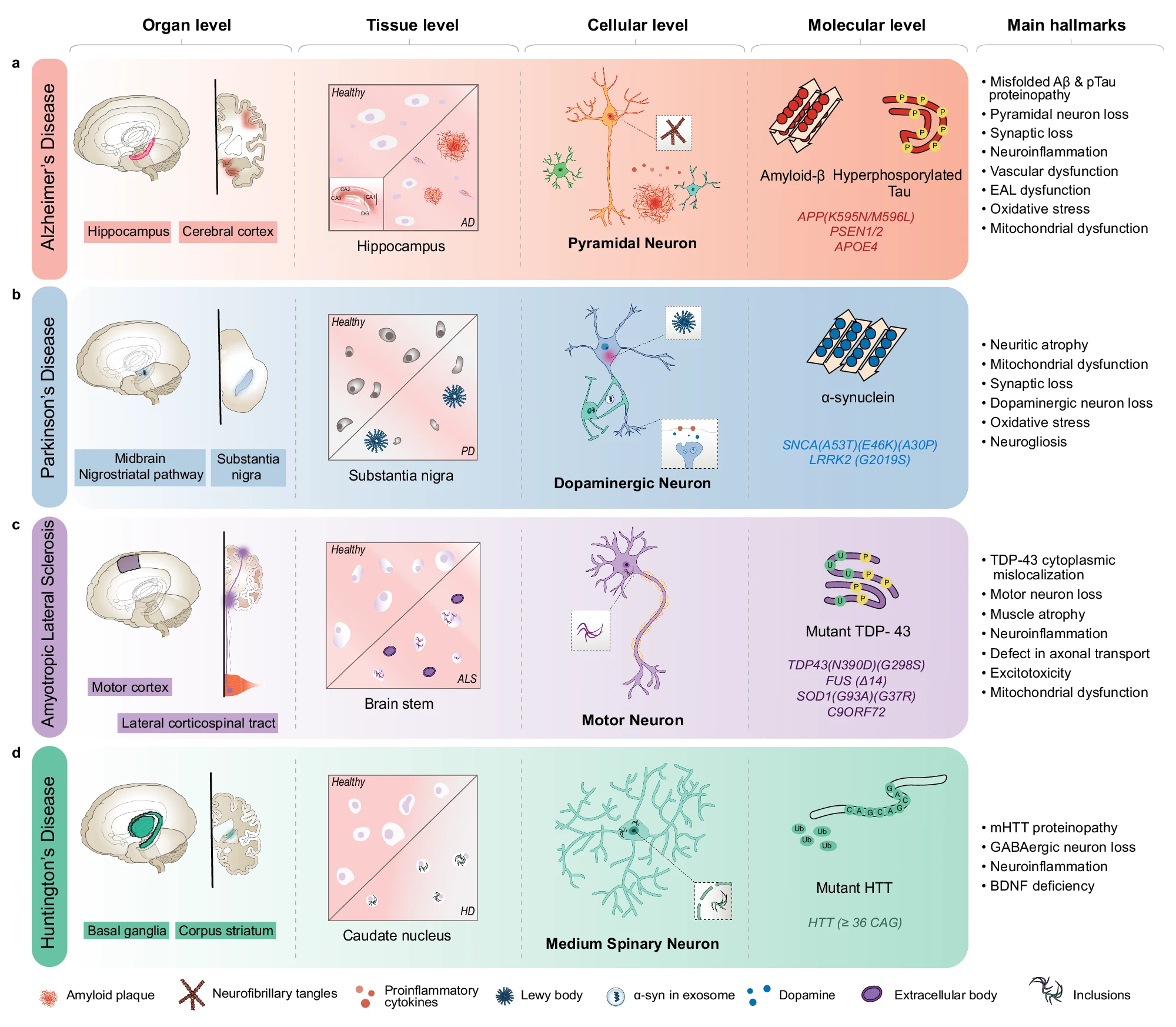
Multi-Modal Approach in Studying Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Multidimensional Perspective
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, are complex, multifactorial conditions that require comprehensive and integrative approaches for effective study and intervention. A multi-modal approach, which combines diverse types of data from genetic to molecular levels, offers a powerful framework for understanding these diseases holistically. This method allows for the examination of intricate interactions between genetic factors, molecular processes, and clinical manifestations, providing deeper insights into disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets.
Genetic Data: SNP Identification, DNA Methylation, and Gene Expression
Genetic data play a crucial role in unraveling the complexities of neurodegenerative diseases. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are variations in the DNA sequence that can influence an individual’s susceptibility to diseases. Identifying SNPs associated with neurodegenerative conditions helps in understanding the genetic risk factors and developing predictive models for disease onset and progression.
-
SNP Identification: SNPs are pivotal in identifying genetic predispositions to neurodegenerative diseases. By analyzing large datasets, researchers can pinpoint SNPs that correlate with increased disease risk. These genetic markers can be used to stratify patients based on their risk profiles and tailor preventive strategies accordingly.
-
DNA Methylation: DNA methylation, an epigenetic modification, plays a significant role in regulating gene expression without altering the DNA sequence. Changes in DNA methylation patterns have been linked to neurodegenerative diseases. Studying these patterns helps in understanding how environmental factors and aging contribute to disease pathogenesis. This knowledge can lead to the development of biomarkers for early detection and intervention.
-
Gene Expression: Gene expression data reveal how genes are turned on or off in response to various factors. Abnormal gene expression patterns are often observed in neurodegenerative diseases. Analyzing these patterns provides insights into the molecular mechanisms driving disease progression and identifies potential therapeutic targets.
Multi-Level Analysis: From Behavior to Molecular Interactions
Neurodegenerative diseases manifest across various biological levels, from behavioral changes to molecular disruptions. A comprehensive approach involves studying these diseases at multiple levels to understand the complex interactions within the biological system.
-
Behavioral and Organ-Level Analysis: Neurodegenerative diseases often present with distinct behavioral symptoms, such as memory loss in Alzheimer’s or motor dysfunction in Parkinson’s. Clinical assessments and neuroimaging techniques provide valuable data on these manifestations. Combining this information with genetic and molecular data helps in understanding how genetic predispositions and molecular alterations translate into clinical symptoms.
-
Molecular-Level Analysis: At the molecular level, disruptions in protein homeostasis, synaptic function, and cellular signaling are critical in the pathology of neurodegenerative diseases. Investigating these molecular changes provides a detailed understanding of disease mechanisms and potential intervention points. Techniques such as proteomics, metabolomics, and transcriptomics are essential in this analysis.
Systems Biology Approach: Integrative and Holistic Analysis
To effectively study the multifactorial nature of neurodegenerative diseases, a systems biology approach is essential. This approach integrates data from different biological levels to construct comprehensive models of disease processes.
-
Data Integration: Systems biology emphasizes the integration of diverse datasets, including genetic, epigenetic, proteomic, and clinical data. This integrative analysis helps in identifying key regulatory networks and pathways involved in disease progression. By understanding these networks, researchers can develop more targeted and effective therapeutic strategies.
-
Advanced Analytical Algorithms: Extracting meaningful insights from multi-modal data requires advanced analytical algorithms capable of handling high-dimensional and complex datasets. Machine learning and deep learning algorithms are particularly suited for this task. These algorithms can identify patterns and correlations that are not discernible through traditional analytical methods.
-
Machine Learning: Machine learning algorithms can analyze large datasets to identify risk factors, predict disease progression, and classify patients based on their disease profiles. These predictive models are invaluable in clinical decision-making and personalized medicine.
-
Deep Learning: Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, excels in analyzing complex data structures such as images and sequences. In neurodegenerative disease research, deep learning algorithms can analyze neuroimaging data to detect early signs of disease, segment brain regions, and identify biomarkers associated with disease progression.
-
Conclusion
The multi-modal approach in studying neurodegenerative diseases provides a comprehensive framework for understanding these complex conditions. By integrating genetic data, molecular interactions, and clinical manifestations, researchers can uncover the intricate mechanisms underlying these diseases. This approach not only enhances our understanding of disease processes but also facilitates the development of predictive models and personalized therapeutic strategies. Advanced analytical algorithms, such as machine learning and deep learning, are crucial in extracting meaningful insights from multi-modal data, paving the way for innovative solutions in neurodegenerative disease research and management.